If you sell products or services to online consumers, you know how important clickability and conversion rates are to your digital marketing strategy. Contextual and behavioral targeting are marketing tools that allow you to place ads in front of consumers looking for your product.
Learning how contextual and behavioral targeting work can change your approach to digital advertising and increase the likelihood of success.
In this article, we'll find out how contextual and behavioral targeting work, look at the benefits of each model and try to decide which is better.

What is contextual targeting?
Contextual targeting is a way to show contextual ads based on website content. Looking for ways to help dry hair? Great, it'll show you an ad for a new hair styler or an article about trendy hairstyles. It depends on what keywords will be found on the website page.

There are two types of contextual targeting.
Keyword audience targeting
Keyword contextual targeting focuses on analyzing the semantics of the content and identifying keywords or phrases on the page.
Ad Targeting by Category
This is a type of targeting in which contextual advertising is targeted to web pages that fit into pre-assigned headings or categories.
Here's how it works:
- A search algorithm scans the web and categorizes pages based on semantics;
- When a user visits a page, information about that page's content reaches the ad server, which matches it with relevant contextual advertising based on keywords.
This method helps you place your brand in the right place and at the right time to get maximum exposure.
It also gets better results because it allows you to place contextual ads in front of your audience without being pushy.
Why use contextual targeting
There are three main reasons you should choose contextual targeting in your next campaign.
- It's cost-effective;
- It's safe;
- It offers more personalization.
It's cost-effective
Entrepreneurs spend a portion of their budget on media advertising to increase brand awareness and sales. With such a large investment, you probably want your campaign to attract qualified leads to your landing pages.
Contextual advertising focuses only on visitors currently exploring topics related to your brand. This reduces the cost of attraction by ensuring that your contextual advertising doesn't end up on random pages.
It's safe
Popular browsers like Firefox and Safari have long restricted third-party cookies to track your potential customer's behavior.
And not too long ago, Google also announced an initiative called "Privacy Sandbox", which will eventually make third-party cookies outdated.
While this announcement was good news for users of this search engine, it was a major test for advertisers, who typically rely on cookies to track their audience's preferences.
Since contextual advertising solutions don't need cookies to measure visitor behavior, you don't have to worry about future changes affecting your PPC campaign.
It's personalized
People see hundreds of contextual advertisements daily, and hardly 10% find them interesting enough to click on a banner. In such a tough market, personalization is the only way to get your target audience's attention.
Contextual targeting changes the placement of your contextual ads based on the topic you are interested in.
It allows you to choose topics that will make your products more appealing to your potential customers, such as offering resin tools on a DIY jewelry blog.
Examples of Contextual Advertising
Now that we have a general idea of contextual targeting let's look at examples of contextual advertising with contextual targeting to see different ways to use media advertising to reach your target audience.
1. Cartier Women
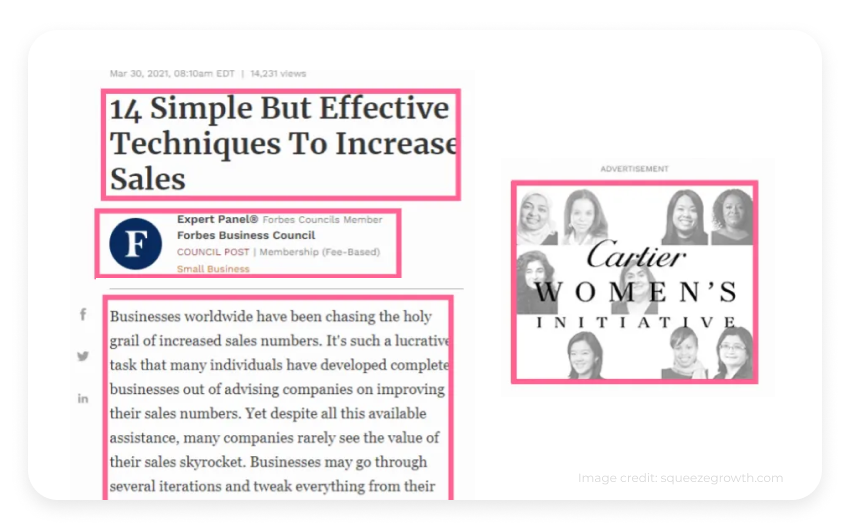
The Cartier Women contextual advertising post is a perfect example of how to highlight your brand with location, topics, and keyword targeting.
In the above case, the blog is the location, Forbes is the business category, while the "technique to increase sales" is a related phrase that matches the brands and purpose of the blog.
Here, the advertiser took advantage of women entrepreneurs' desire for growth to customize ad placement.
Blogs are commonly used for contextual advertising because 60% of visitors read them to get the information they want. By choosing your keywords carefully, you can greatly increase your click-through rates.
2. The Spruce Eats
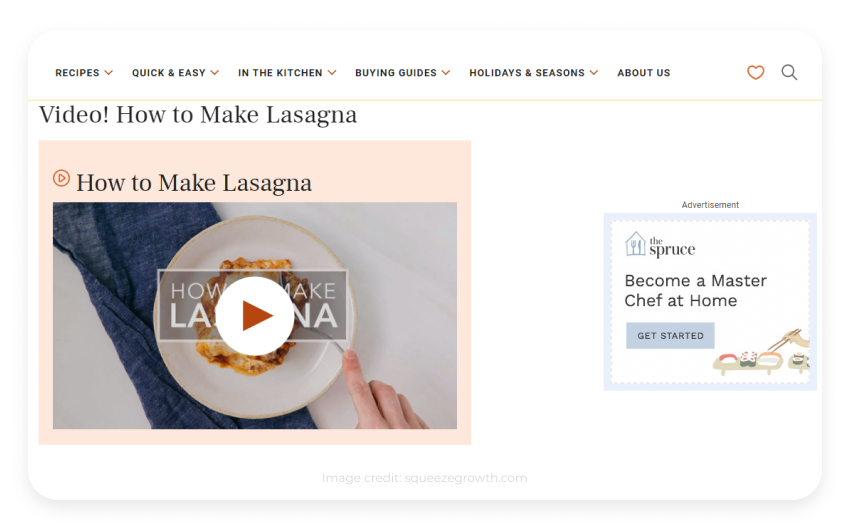
The Spruce Eats is a food site that makes its money by selling kitchen tools and recipe books. It is aimed at gourmet cooks who love to cook and want to learn different tools to use in their everyday lives.
The screenshot above shows that the company has advertised the brand on another cooking blog with practical tips that target a similar audience.
With this ad, Spruce targeted amateur chefs looking for lasagna recipes and attracted them with a more appealing offer: "Become a chef at home".
This example demonstrates the combined effect of contextual targeting and compelling text.

What is behavioral targeting?
Behavioral targeting is an algorithm that most ad networks use when displaying ads. The essence of the technology is to show users behavioral advertising based on their interests.
Behavioral targeting allows you to show relevant creatives to interested users. Adapting to each user's interest rather than a segment.
Companies use behavioral advertising to target customers based on their online behavior, such as the purchases they make, the websites they visit, and their search queries.
For example, if a user views a pair of athletic shoes on an e-commerce site, the company can then show them digital advertising on other sites, increasing the likelihood that they will end up making a purchase.
Behavioral campaigns serve ads to get user interest from two sources:
Proprietary behavioral data
This data includes sites the user visits, the time they spend, and actions they take. And most importantly, how long ago it was because the user's interest in the topic is not eternal.
The advertisement will depend directly on the sites the user views. If the user's preferences change, then behavioral advertising changes.
For example, 2 days ago, the user was interested in teapots and visited tea-related sites. The mechanism will consider that and show relevant digital advertising related to teapots and tea.
External supplier data (DMP)
DMP (data management platform) is a platform that collects data about different audiences segmented by category, age, interests, behavior, and other attributes. Such data makes it possible to maximize the target audience of different sizes and thereby increase the effectiveness of contextual advertising. If a user's profile gets to the data provider, you will not be able to hide from behavioral advertising, even in incognito mode.
It is important to remember!
Contextual advertising on behavioral targeting can be shown even on sites that belong to a different subject.
Contextual vs. Behavioral Targeting
Behavioral targeting uses third-party cookies to track the type of sites you've visited and, based on that information, displays relevant digital ads multiple times to get your attention.
It's an effective form of retargeting that generates 6.8% more conversions than other types. But there is a big disadvantage. Displaying the same ad multiple times often generates opposite and negative reactions.
Many people find retargeting behavioral ads useful because they offer them what they are looking for, but 54% still feel intimidated by their level of accuracy.
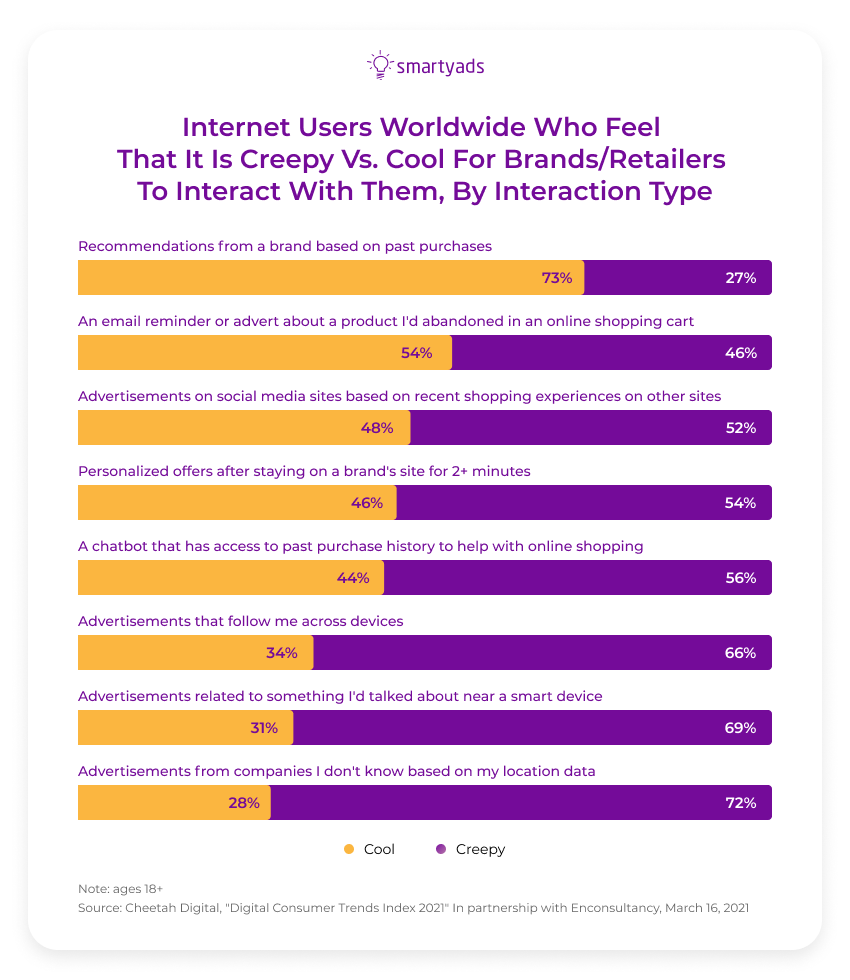
On the other hand, contextual targeting uses non-invasive methods.
Instead of focusing on online behavior, it scans your keywords with host pages and shows your ad on sites using exact words or sub-contexts.
So if you sell herbal shampoos, your ad will only appear on hair care or health and beauty products sites.
Think of it as SEO optimization.
In fact, a search engine post is a classic example of contextual advertising! (Almost).
It doesn't appear randomly in your browser unless you type in a specific keyword or question.
Why use behavioral targeting?
Behavioral targeting offers several powerful benefits for ad campaign settings.
Retargeting
With this technology, an advertiser can show a consumer the same ad on different sites. This allows the advertiser to show the consumer the product multiple times, increasing the likelihood of purchase.
Personalized behavioral advertising
The advertiser shows ads to the consumer based on their online activity. Since the behavioral ads shown by the brand match the consumer's past behavior and interests, this form of behavioral advertising usually has a higher conversion rate. It also creates a better user experience.
Benefits of behavioral targeting
There are several key benefits of behavior-based targeting of consumers. The main benefits are:
Increase user engagement: behavioral targeting allows companies to target consumers based on their habits. Since the ads consumers see are more consistent with their past behavior and interests, they are more likely to engage with them.
Higher click-through rates: as this contextual advertising aligns with consumers' browsing and buying behavior, they are more likely to click on the ads displayed to them.
Higher conversion rates: ads targeted to a behavioral target market tend to appeal to consumers who view them. This increases the likelihood that the user will either request more information about the product or service or make a purchase.
Improved perception of contextual advertising: when users are shown more personalized contextual advertising, they tend to find viewing more enjoyable, increasing the viewing experience and user satisfaction.
Higher sales: Companies that use behavioral targeting tend to get higher sales. They can easily alert customers to relevant products and inform them about brands they have previously shown interest in. They can also capture sales from users who viewed products but left the web page before completing the checkout process.
How behavioral targeting works
Here's a look at the behavioral targeting process in three steps:
1. Collecting Data
The first step in the behavioral targeting process involves collecting personal user data from multiple sources. The data comes from CRM systems, websites, mobile apps, and other marketing automation systems. The types of data companies collect include:
Frequently visited pages: companies can track whether a user visits a web page once, repeatedly, or regularly.
Web browsing time: by tracking the amount of time someone spends on a website, companies can learn more about their interest in certain products or services.
Clicked ads or links: advertisers can track the ads and links a visitor clicks on. This can help the advertiser know which marketing language and images are most effective in attracting users' attention.
Website Element Interaction: companies can learn which elements on their website cause the most interaction with the user. For example, they can see which icons, navigation bars, menus, images, and video content get the most clicks from users.
Transaction progress: companies can see when users place items in their carts to identify when users have not completed the checkout process. Advertisers can then show these users ads on other pages to encourage them to return and make a purchase.
Purchases: behavioral targeting allows companies to target shoppers with ads for products they predict may interest the consumer.
The amount of time between visits: a company can track the time between visits to their site. If they notice a short time between visits, they can infer that the user has a pressing need for their product or service.
Companies use special types of third-party cookies or tracking pixels to collect this information. Once companies collect the information, they can analyze and segment it.
2. Visitors are divided into segments
The second step in the behavioral targeting process is segmentation. Companies can divide consumers into different segments based on browsing or buying behavior.
For example, if an e-commerce site sells different types of cosmetics, a company might put people who look at beauty care products in one category, people who look at makeup products in another, and people who actually bought cosmetics in a separate category.
3. Applying the data
In the last step of the behavioral targeting process, a company can develop unique contextual advertising campaigns based on their created segments. It allows them to develop ad campaigns highly relevant to the users they are targeting. Not only does this add personality to their ad campaigns, but it also increases the likelihood of user engagement and, ultimately, conversion rates.
What to choose?
It is impossible to say for sure what is better for a particular brand or a particular advertising campaign.
On the one hand, behavioral targeting focuses more on interests and analyzing past user behavior, so it collects more conversions, but on the other hand, contextual targeting does not depend on cookie files and less scares users with its "all-vision".
Only you can know which targeting is best for you and your brand. Our task is to tell you about the options and possibilities for using the tools we have. We hope you will be able to use targeting to achieve your goals.
Launch ad campaigns and set up programmatic targeting with SmartyAds.




